[toc]
I. Introduction
The IoT Connectivity Challenge
In the ever-expanding realm of the IoT, a crucial challenge lies in connecting low-power devices over vast distances. Enter LPWAN, LoRaWAN, and LoRa – a trio of technologies vying for dominance in this intricate landscape. This guide unravels the complexities, empowering you to choose the ideal solution for your low-power, wide-area IoT needs.
The Low-Power, Wide-Area Conundrum
The growing number of battery-powered IoT devices demands solutions that balance long-range communication with minimal power consumption. Traditional cellular networks, while offering broad coverage, are often power-hungry for battery-powered devices. To address this, LPWAN technologies have emerged, offering an optimal blend of extended range and energy efficiency. They provide the backbone for countless applications, from smart agriculture to industrial automation, where devices need to operate independently for extended periods without frequent battery replacements.
II. LPWAN: The Low-Power Wide-Area Network Landscape
The Big Picture
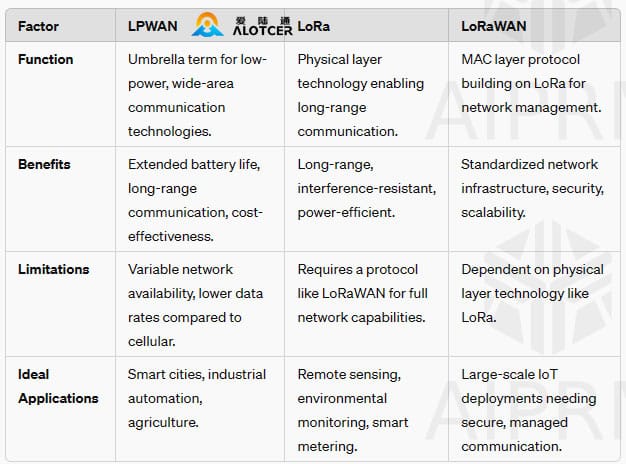
LPWAN, or Low-Power Wide-Area Network, is a category of wireless communication technologies designed specifically for low-power, long-range applications. These networks excel in connecting devices that require minimal data transmission over vast distances, making them ideal for IoT deployments in diverse environments such as rural areas, urban landscapes, and industrial sites.
Benefits of LPWAN
Extended Battery Life
LPWAN technologies enable battery-powered devices to operate for years on a single charge, significantly reducing maintenance efforts and costs. This is particularly beneficial for applications like environmental monitoring, where devices are deployed in remote or hard-to-reach locations.
Long-Range Communication
One of the standout features of LPWAN is its ability to connect devices across vast distances, often several kilometers, even in challenging conditions. This makes it an excellent choice for applications that require wide-area coverage without the need for extensive infrastructure.
Cost-Effectiveness
LPWAN solutions are cost-efficient, offering a scalable option for connecting a large number of low-data-rate devices. This affordability is critical for large-scale IoT deployments, where the cost per device must be minimized to achieve economic viability.
A Glimpse into LPWAN Technologies
While LoRaWAN is one of the most recognized LPWAN technologies, other notable contenders include Narrowband-IoT (NB-IoT) and Sigfox. Each of these technologies has unique strengths and use cases, catering to different aspects of IoT connectivity requirements.

III. LoRa: Unveiling the Physical Layer
LoRa Defined
LoRa, short for Long Range, is a physical layer technology used in some LPWAN solutions. It is akin to the foundation on which a house is built, providing the fundamental structure for data transmission. LoRa operates in the unlicensed ISM (Industrial, Scientific, and Medical) radio bands, making it accessible and cost-effective.
LoRa’s Magic: Spread Spectrum Modulation
The core of LoRa’s effectiveness lies in spread spectrum modulation. This technique involves breaking down data into smaller packets and transmitting them over a wider bandwidth. The result is a robust communication method that offers:
- Longer Range: LoRa can communicate over several kilometers, even in dense urban environments.
- Better Interference Resistance: The spread spectrum approach helps LoRa signals avoid interference from other wireless devices, ensuring reliable data transmission.
- Efficient Power Consumption: By optimizing transmission methods, LoRa ensures that devices use minimal energy, extending battery life.
These features make LoRa particularly suited for applications requiring reliable, long-range communication without the need for significant power consumption.
IV. LoRaWAN: The Mastermind Behind the Network
LoRaWAN Explained
LoRaWAN is a media access control (MAC) layer protocol that builds upon LoRa to create a standardized network infrastructure. Think of LoRa as the engine and LoRaWAN as the vehicle that transports data efficiently and securely across the network. LoRaWAN handles the higher-level functions such as data routing, device authentication, and security.
The LoRaWAN Orchestra
A LoRaWAN network comprises several key components, each playing a vital role in ensuring seamless communication:
- End Devices: These are the battery-powered IoT sensors and actuators that communicate using LoRa technology. They send data to gateways, which then relay it to the network server.
- Gateways: Acting as intermediaries, gateways receive data from end devices and forward it to the network server. They also transmit commands from the network server back to the end devices.
- Network Server: This central hub manages communication between end devices and applications. It handles data processing, device authentication, and security, ensuring reliable and secure network operation.
Together, these components form a cohesive system that facilitates efficient, long-range IoT communication.
V. LPWAN vs. LoRaWAN vs. LoRa: A Comparative Analysis
VI. Choosing the Right Champion: Factors to Consider When Making Your Decision
Network Coverage
Before selecting a technology, evaluate the availability of existing LPWAN networks (like LoRaWAN) in your target deployment area. The presence of a robust network infrastructure can significantly reduce deployment costs and complexity.
Data Rate and Latency Requirements
Consider the amount of data your devices need to transmit and the acceptable delay in communication. LPWAN technologies generally support low data rates, which is sufficient for applications like environmental monitoring but might not be suitable for high-data-rate needs.
Device Battery Life
Prioritize technologies that offer the longest possible battery life for your resource-constrained devices. LoRaWAN, for example, is optimized for ultra-low power consumption, making it ideal for applications where devices are expected to operate for years on a single battery charge.
Security Needs
Assess the security features offered by different LPWAN solutions to ensure data integrity and privacy. LoRaWAN includes built-in security mechanisms like AES encryption and mutual authentication, providing robust protection against unauthorized access.
Cost Considerations
Compare the upfront costs of devices and network access fees associated with each LPWAN technology. While some technologies might have higher initial costs, their long-term benefits, such as reduced maintenance and longer device lifespan, could offer better value.
VII. Beyond the Basics: Exploring Additional LPWAN Applications
Smart Cities
LPWAN technologies can transform urban infrastructure management by enabling smart city applications such as:
- Traffic Flow Monitoring: Sensors can track vehicle movement, helping optimize traffic signals and reduce congestion.
- Parking Availability: IoT devices can provide real-time updates on parking spaces, improving convenience for drivers.
- Environmental Conditions: Air quality and noise level sensors can help city planners address pollution and enhance urban living.
Industrial Automation
In industrial settings, LPWAN can revolutionize operations by connecting sensors for:
- Remote Monitoring: Track equipment performance and asset locations, enabling proactive maintenance and reducing downtime.
- Preventive Maintenance: Sensors can detect potential issues before they cause failures, improving overall operational efficiency.
Agriculture
LPWAN’s long-range communication capabilities are particularly valuable in agriculture for:
- Precision Agriculture: Monitor soil moisture, weather conditions, and crop health to optimize irrigation and fertilization, increasing yield and reducing resource use.
- Livestock Management: Track the location and health of animals, ensuring timely interventions and improving overall herd management.
VIII. FAQs
Is LoRa the same as LoRaWAN?
No, LoRa is a physical layer technology that provides the foundation for communication, while LoRaWAN is a network protocol that builds on top of LoRa to manage communication between devices and applications.
Which LPWAN technology is the best?
There’s no single “best” option. The ideal choice depends on your specific needs, considering factors like network coverage, data requirements, battery life, security, and cost.
Can I use my existing Wi-Fi network for LPWAN communication?
No, LPWAN technologies are specifically designed for long-range, low-power communication, unlike Wi-Fi which has a shorter range and higher power consumption.
How secure are LPWAN networks?
Security features vary depending on the specific LPWAN technology and network implementation. LoRaWAN offers built-in security mechanisms for data encryption and access control.
What’s the future of LPWAN?
With the ever-growing number of IoT devices, LPWAN technologies are expected to play a crucial role in enabling efficient and scalable communication. Advancements are underway to improve network capacity, security, and integration with cloud platforms.
What is the difference between LPWAN, LoRa, and LoRaWAN?
LPWAN is a broad category of low-power, long-range communication technologies. LoRa is a specific physical layer technology within LPWAN, while LoRaWAN is a network protocol that uses LoRa for data transmission.
Which is better, LPWAN or LoRaWAN?
LPWAN refers to the broad category, while LoRaWAN is a specific technology within that category. The “better” choice depends on your specific application requirements, including range, data rate, and power consumption.
What are the applications of LPWAN technology?
LPWAN technology is used in smart cities, industrial automation, agriculture, environmental monitoring, and asset tracking due to its long-range, low-power communication capabilities.
How much does a LoRaWAN network cost to set up?
The cost of setting up a LoRaWAN network varies depending on factors like the number of devices, gateways, and the area of coverage. However, it is generally considered cost-effective compared to other long-range communication solutions.
What are the security features of LoRaWAN?
LoRaWAN includes robust security features such as AES encryption, mutual authentication, and end-to-end security, ensuring data integrity and privacy.
IX. Conclusion
Empowering Your IoT Vision
Choosing the right LPWAN technology is crucial to powering your IoT applications effectively. Each technology, whether LPWAN, LoRa, or LoRaWAN, offers unique benefits and caters to different aspects of IoT connectivity. By understanding these technologies, you can make informed decisions that align with your specific needs, ensuring efficient and reliable communication for your IoT devices.
A World of Possibilities Awaits
The exciting potential of LPWAN technologies lies in their ability to connect the physical world to the digital realm, fostering innovation and efficiency across various industries. As you embark on your IoT journey, consider the insights provided in this guide to unlock the full potential of your applications, transforming your vision into reality.