What is a Router?
How Routers Work
Imagine the internet as a vast highway system. Routers are the traffic cops, directing data packets to their destinations. They examine the packets’ addresses, determine the best route, and forward them along the network. This process, known as packet switching, ensures efficient data transmission.
Key Components of a Router
CPU: The brain of the router, responsible for processing data packets and making routing decisions.
Memory: Stores routing tables, configuration settings, and temporary data.
Network Interfaces: Connect the router to other devices, such as computers, switches, and other routers.
The Industrial Router: Built for the Demands of Industry
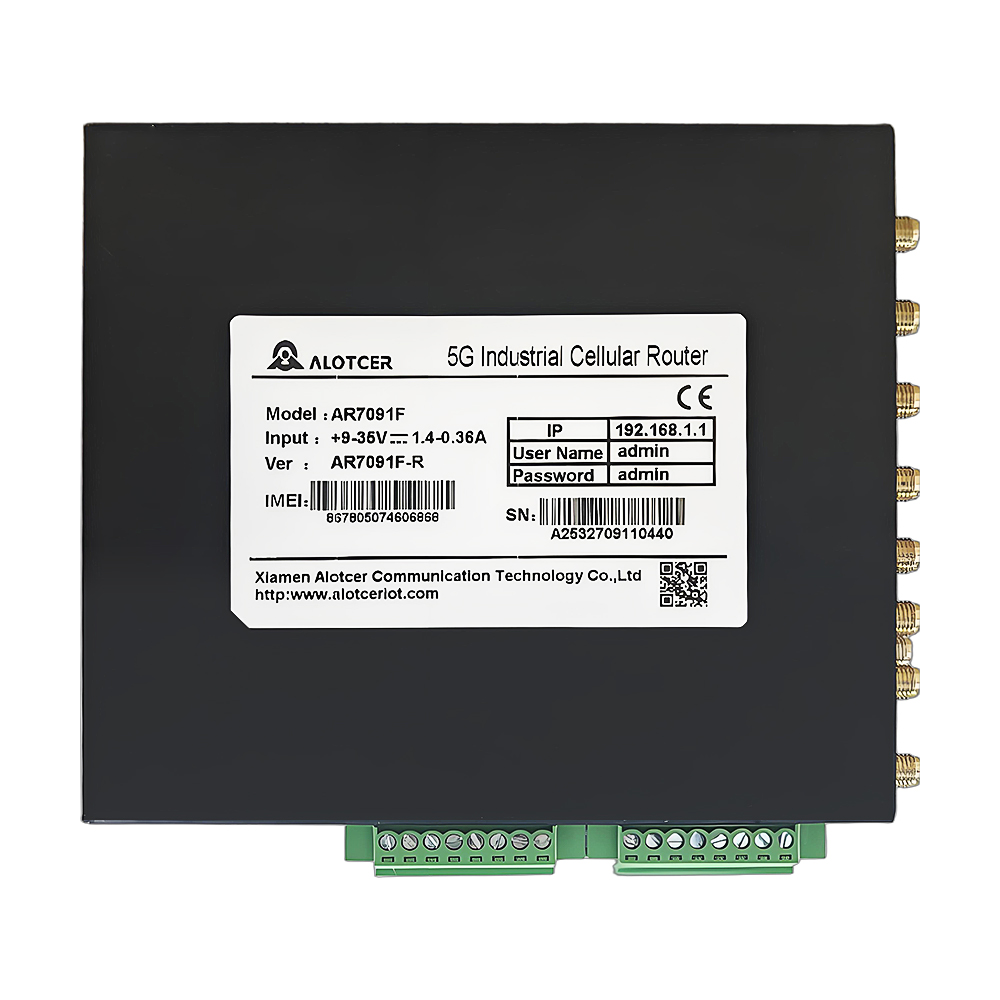
Alotcer router with remote access-AR7091
An industrial router is a specialized networking device designed to meet the rigorous demands of industrial environments. It offers robust connectivity and reliability, ensuring seamless data transmission in challenging conditions such as high temperatures, humidity, and electromagnetic interference. industrial router is the integration of a “router with remote access,” which allows for secure, remote management and monitoring of industrial systems.
Unique Features of Industrial Routers
Rugged Design: Industrial routers are built to withstand harsh environments, including extreme temperatures, humidity, and vibrations.
Wide Temperature Range: They can operate reliably in a wide range of temperatures, from freezing cold to scorching hot.
Advanced Security: Industrial routers are equipped with robust security features, such as firewalls, VPNs, and intrusion detection systems, to protect sensitive industrial data.
High-Performance Hardware
Powerful Processors: Industrial routers often have powerful processors to handle heavy traffic loads and complex routing protocols.
Ample Memory: They require ample memory to store large routing tables and configuration settings.
Advanced Routing Protocols
Dynamic Routing: Industrial routers use dynamic routing protocols, such as OSPF and BGP, to automatically adapt to network changes and optimize routing decisions.
Redundancy and Failover Mechanisms:Ensuring Continuous Connectivity: Industrial routers often employ redundancy and failover mechanisms to ensure continuous connectivity, even in the event of hardware failures.
Robust Security Features:Protecting Sensitive Industrial Data: Industrial routers are equipped with a variety of security features to protect sensitive industrial data from cyber threats.
The Home Router: Designed for Residential Use
Basic Functionality
Connecting Devices to the Internet: Home routers connect devices like computers, smartphones, and smart TVs to the internet.
Sharing Network Resources: They allow devices to share network resources, such as printers and storage devices.
Limited Processing Power and Memory:
Suitable for Home Use: Home routers have limited processing power and memory, which is sufficient for home use but not for heavy industrial loads.
Simple Routing Protocols
Static Routing: Home routers typically use static routing, which requires manual configuration of routes.
Consumer-Grade Security:Adequate for Home Use: Home routers offer basic security features, such as firewalls and Wi-Fi encryption, which are adequate for home use but not for industrial applications.
Key Differences Between Industrial and Home Routers
The Difference Between Industrial Routers and Home Routers
Real-World Applications of Industrial Routers
Remote Monitoring and Control of Industrial Equipment: Industrial routers enable remote monitoring and control of industrial equipment, such as sensors, actuators, and PLCs.
SCADA Systems: They are used in SCADA systems to collect and transmit data from various industrial processes.
IoT Deployments: Industrial routers are essential for IoT deployments in industrial settings, allowing seamless communication between IoT devices. Whether it’s connecting sensors to monitor environmental conditions, enabling machines to communicate with each other for optimized production, or integrating smart meters for energy management, industrial routers provide the robust and secure connectivity needed to support these advanced applications. They ensure that IoT devices can reliably exchange data, enabling smart factories and other industrial environments to operate more efficiently and effectively.