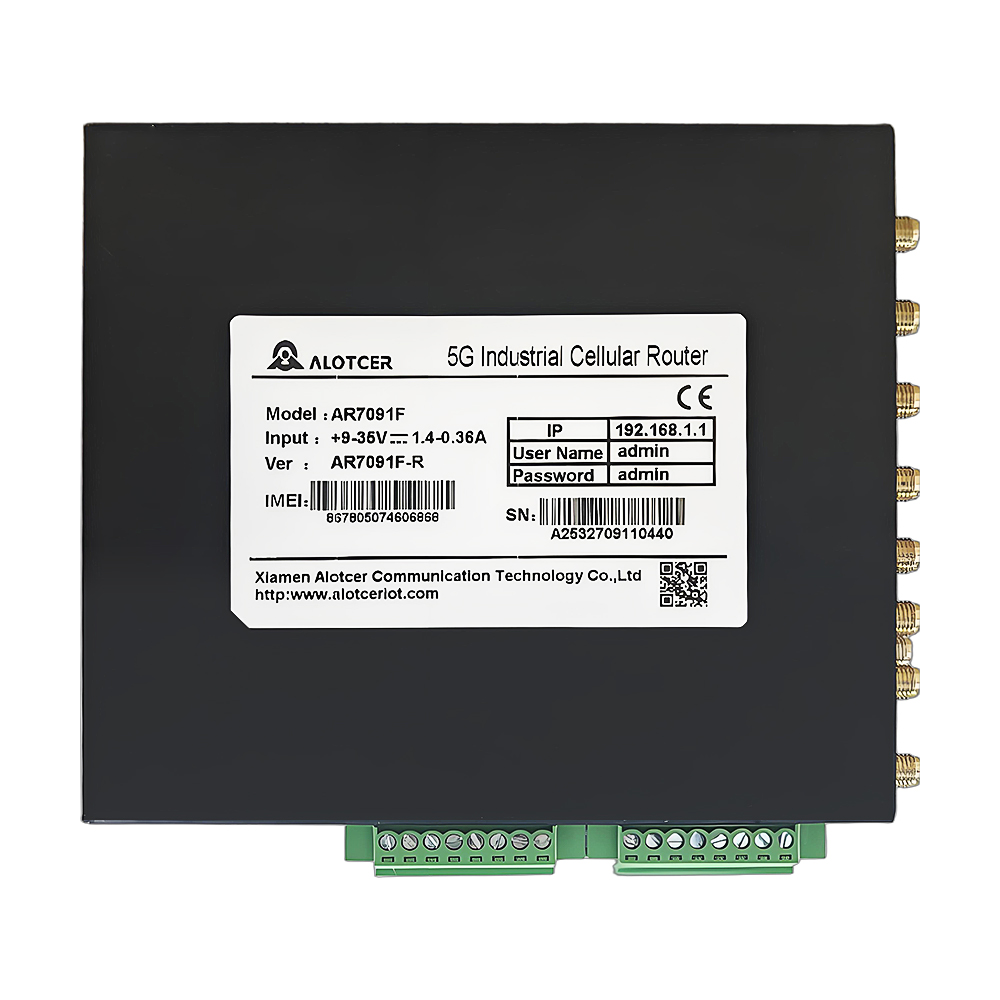
Think of an industrial router as a tireless steward that lives among giant machines. Its only job is to connect every sensor, PLC and server so they can “talk” to one another. Instead of children passing notes through a big brother, steel arms and assembly lines exchange complex data streams through this rugged box. The messages are far more complicated than human words: temperatures, torque values, alarm codes, video feeds, cloud commands.

-
Hardware performance = a healthy body
If the body is weak, work is slow. The same rule applies to the router.1.1 CPU – the brain
A powerful multi-core processor can juggle thousands of packets at once; a cheap chip stalls the same way a muddled brain forgets what it was doing.1.2 RAM – the stomach
More memory lets the router “eat” large data bursts without choking. When RAM is small, packets are dropped and re-transmitted, cutting effective speed.1.3 Network interfaces – mouth & ears
Gigabit or 10-Gb Ethernet ports speak ten times faster than 100 Mb ports. Wi-Fi 6 radios move data like a modern 5 G phone call, while older Wi-Fi 4/5 feel like a crackling land-line. -
Harsh network environment = a rough road
Even a strong body slows on a bad road.2.1 Electromagnetic noise
Motors, welders and drives spray invisible “static.” Good routers use shielded housings, high-gain antennas and cable ferrites—the industrial version of noise-cancelling earphones.2.2 Congestion
When hundreds of sensors shout at once, packets collide. Bandwidth management and VLAN “priority lanes” let alarm codes race through while routine logs wait politely. -
Software tuning = teaching smarter habits
Fast workers use better methods; routers rely on smarter code.3.1 Routing algorithms
OSPF, RIP, BGP or proprietary mesh pick the shortest, least-jammed path the way a GPS avoids traffic.3.2 QoS policies
Quality-of-Service labels critical packets (safety interlocks, video alarms) “express mail,” while bulk firmware updates ride the slow truck. -
Security vs. speed – locking the door without fumbling for keys
Strong locks protect data, but heavy chains slow the courier.4.1 Firewall
Hardware-accelerated firewalls and rule optimization inspect only suspicious flows, letting trusted traffic sprint through.4.2 Encryption / authentication
AES-256 wraps top-secret data in thick steel; lighter AES-128 or null encryption carries low-risk telemetry. Choose the armor that matches the threat.
In short, an industrial router is only as fast as its weakest link—CPU, memory, ports, environment, software or security policy. Balance them all and your factory floor talks at lightning speed, 24 × 7, without ever losing its voice.